No one can deny that the world has changed significantly over the past 50, 30, or even 10 years. Previously, slow and steady won the race, now instant gratification is accelerating various aspects of everyday life.
Unsurprisingly, the way people and businesses interact with payments has also evolved. Where same-day deliveries are routine and global conversations and commerce happen in real-time, waiting several days to receive money no longer makes sense.
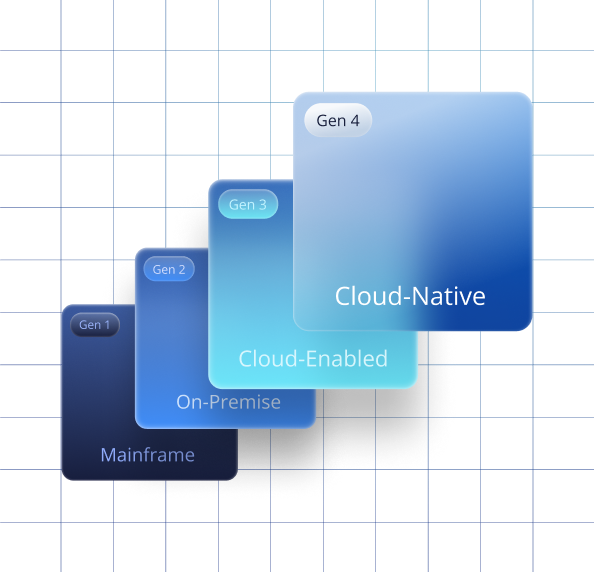
Legacy payments systems grapple to meet these new demands for fast, scalable payments; they are slow to change, slow to process, lack security, and are highly fragmented. To adapt, payments schemes and financial institutions globally are modernising their systems to align and keep up with evolving consumer needs and expectations.
The backbone of modernised payments
Modernisation is primarily driven by three key principles: speed, interoperability, and trust.
- Speed: Cloud-native technology provides faster payments processing.
- Interoperability: Common system language ensures efficient message handling.
- Trust: Transparent processes with complete and accurate payments information.
ISO 20022 is the latest global financial messaging standard accelerating the modernisation of global payments and reporting. Unlike legacy message types, which prioritised character limitations for mainframe processing, ISO 20022 leverages extensible markup language (XML) to support structured and detailed financial messages. This design enables payments modernisation in the following ways:
SpeedStructured messages improve straight-through and automated processing. Machine-readable data is processed faster, reducing latency. Human-readable data allows quicker manual resolutions. |
InteroperabilityStandardised data enables consistent financial messages that are understood and seamlessly processed by different payments systems, schemes and services. |
TrustBanks, fintechs and financial institutions can exchange complete and accurate payment details. Precise and detailed transaction data enhances compliance checks and fraud detection. |
A business driver with established use cases
There is a cost to standing still. ISO 20022 is firmly established in existing schemes and payment methods that are driving business growth today. Ignoring or limiting investment risks widening the gap between competitors. The following use cases showcase where ISO 20022 has been used as the foundation for payments modernisation:
Low-value, instant payments
Instant payments are expected to grow by 161% between 2024 and 2028. To facilitate rapid transaction processing, instant payments schemes are ISO 20022 enabled and are supported by future-fit, cloud-native infrastructures.
With ISO 20022, complementary services such as Request-to-Pay (RTP) are implemented to support instant payments adoption and enhance the consumer and merchant experience. With the extra space and structured data, RTP messages can contain detailed payment references, due dates, and additional data, reducing disputes and manual reconciliation.
API-based payments and Open Banking
Global Account-to-Account (A2A) payments are expected to grow by 230% between 2024 and 2029. These API-based payments rely on real-time authentication and speed to process secure and instant bank-to-bank payments. ISO 20022 ensures both speed and trust by enabling interoperability between banks while maintaining compliance through transparent payment details.
Similarly, Open Banking requires interoperability for banks, fintechs, and third-party payment providers (TPPPs) to collaborate in delivering competitive financial services. Instead of operating in siloed platforms, ISO 20022 allows these entities to exchange standardised and structured data securely, providing service providers with a holistic view of their customer’s financial position, behaviour, and preferences.
High-value cross-border and domestic payments
By 2018, over 70 countries implemented ISO 20022 payments schemes to improve local payments. Still, disparities in payments schemes and varying country-specific compliance requirements have slowed global payments. Aggravating the issue, the Swift Message Type (MT) format, developed in the 1970s, has limited character space, leading to truncated or incomplete messages between banks and financial institutions.
Recognising the need to improve high-value settlements globally, Swift mandated participant banks to migrate all MT cross-border payments and reporting messages to ISO 20022 by November 2025. Following the announcement, the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) mandated all South African Multiple Option Settlement (SAMOS) system participants to migrate local high-value payments and reporting messages to ISO 20022. This transition was completed ahead of major currencies in September 2022.
Why is it a strategic advantage for South African banks?
South Africa has made significant progress in implementing ISO 20022, with almost all payments schemes already enabled. This positions the ecosystem well for future advancements and creates a competitive payments market.
Local banks need to evaluate how prepared their systems are for looming changes that will require ISO 20022 implementation such as:
- Increasing PayShap and PayShap Request adoption: Soon, it will be essential for all banks to support this instant payment method.
- Enhanced regulatory compliance: The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) grey-listing of South Africa highlights the need for rich and accurate financial information to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) modernisation: Except for cards, EFT is the only electronic payment method that is on a proprietary message standard. The 180-byte message restricts the ability to carry complete financial data for each transaction. Banks must prepare for a new or enhanced ISO 20022 scheme that meets regulatory requirements. Banks need to prepare their systems to adapt to a new or revamped ISO 20022 enabled-scheme that better meets regulatory and compliance requirements.
- Instant cross-border payments within the Southern African Development Community (SADC): BankservAfrica TCIB, an ISO 20022-based instant payments system, supports low-value cross-border payments. As remittances gain popularity due to increased migration, this system has the potential to facilitate millions of transactions through the banking sector.
Modernising core systems is a smart money move
ISO 20022 is not just a technical upgrade - it is the foundation for the future of payments. Its ability to enhance speed, interoperability, and trust makes it a critical enabler of modernised financial ecosystems.
For South African banks and financial institutions, continued investment in ISO 20022-enabled, cloud-native systems will be essential to remain competitive and compliant in the evolving payments landscape.
Modernising banking systems can be complex and time-consuming, diverting valuable resources away from core business goals. While system modernisation is necessary, focussing on what sets your bank apart is essential to drive revenue and growth. Electrum’s next-generation payments technology helps leading banks fast-track their ISO 20022 adoption and implement future-proof, cloud-native payments solutions. By partnering with us, you can achieve the speed, interoperability, and trust needed to lead in modern payments - without compromising your focus on delivering value to customers.
Future-proof your payments with cloud-native technology.

Kganya Molefe
Kganya is a freelance Content Writer based in Johannesburg with experience in African Payments. When she’s not writing, Kganya enjoys journaling the old-fashioned way, listening to podcasts during her long walks, and passionately discussing the importance of low-cost, real-time, pan-African payment solutions with her friends and family.
Electrum Newsletter
Quarterly insights and news to help you keep up with the latest changes in the payments landscape